This week we broke the news that chytridiomycosis, a rapidly spreading amphibian disease, has reached a site near Panama’s Darien region, leaving us little time to save the species there at risk of extinction. Here’s an updated map of how the pathogen is moving through the neotropics:
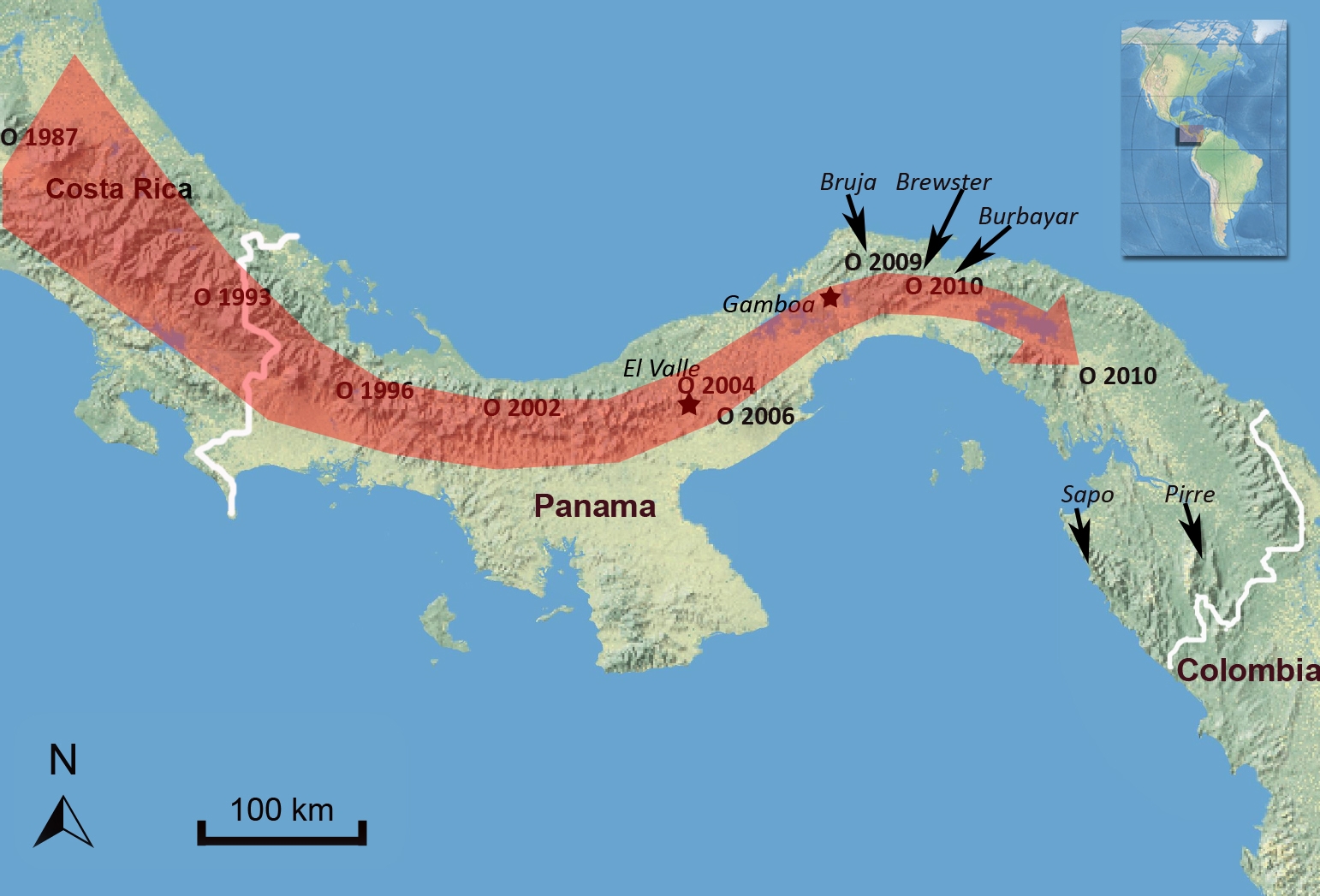
Chytridiomycosis has been linked to dramatic population declines or even extinctions of amphibian species worldwide. Within five months of arriving at El Cope in western Panama, chytridiomychosis extirpated 50 percent of the frog species and 80 percent of individuals.
Conservationists have been fretting for years about what might happen to Eastern Panama’s 120-odd amphibian species when chytrid hits. Chytrid is a disease that cannot tolerate extremely hot temperatures, so it tends to be most devastating in cooler mountainous regions of the tropics that remain cool and moist year-round. The mountainous regions of Eastern Panama are one of the last remaining strongholds of naïve amphibian populations in the New World, and species that tend to have a highland distribution and small ranges are the most vulnerable to extinction.
